Synthesis of cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant. The two most well-known cannabinoids are CBD and THC, which form the entire industry. In addition to those, scientists have already discovered hundreds of cannabinoids. Only a few of them have an intoxicating effect; most cannabinoids, in contrast, offer various health benefits. As the popularity grows and clinical trials commence, new potential uses are continually being discovered.
However, many cannabinoids are challenging to isolate from the Cannabis sativa plant due to their rare nature. Specialists referred to them as rare cannabinoids, and many of them offer unique properties, applications, and benefits. Exploring these rare compounds has led to endless possibilities for consumer and medicinal applications.
Potential benefits of cannabinoids
The human body contains different cannabinoid receptors that help regulate critical processes, including learning, memory, neuronal development, appetite, digestion, inflammation, overall mood, sleep, metabolism, and pain perception. This considerable involvement of cannabinoid receptors, critical to many physiological systems, underscores their potential as pharmaceutical targets.
The result: high quality and high quantity of rare cannabinoids.
By creating a strain of oily yeast that contains these compounds, we achieved a greater yield, higher quality, and a more sustainable production process. This process can be easily upscaled to produce larger volumes of pure rare cannabinoids that can be used in countless products across a wide variety of industries. Using a biosynthetic method to create these cannabinoids will ultimately allow these beneficial compounds to reach more people while minimizing environmental impact, cost, and resources. Our proprietary biosynthesis process and strain of proprietary yeast serve as a reliable source of pure low-cost clinical-grade cannabinoids biologically identical to those found in nature.
Biomedican’s cutting-edge biotechnology methods are remodeling the production of high-value compounds. Our team of dedicated scientists has genetically optimized yeast to produce cannabigerol (CBG), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), other rare cannabinoids, and analogs. These biosynthetic compounds are pharmaceutically pure and 100% identical to ones found in nature at a fraction of their cost, making them promising contenders to replace synthetic and plant-extracted analogs.

Pharmacology
Pharmacological research has uncovered several medical uses for cannabinoids, which bind to cannabinoid receptors. They’ve been shown to help with pathological conditions such as pediatric epilepsies, glaucoma, neuropathic pain, schizophrenia, and have anti-tumor effects, and promote the suppression of chemotherapy-induced nausea. This ongoing research is becoming more prevalent and can potentially uncover therapeutic uses for an array of cannabinoids.

Food and cosmetic industries
In addition to the medical field, other prominent sectors have adopted the use of cannabinoids. There is an increasing demand for cannabinoids in inhalable, food, and hygienic and cosmetic products. Veterinary services for cannabinoids are also prevailing. The use of naturally occurring cannabinoids reduces the need for synthetic alternatives that may produce harmful off-target effects.
What is cannabinoid synthesis?
Rare cannabinoids exist in minimal quantities in cannabis plants, making their extraction and purification inefficient, costly, and environmentally taxing. It takes 10 kilograms of cannabis plants to produce less than 2 grams of rare cannabinoids. Cannabis cultivation is labor, time, and energy-intensive and can produce inconsistent yields prone to contamination from pests, mold, and pesticides. Significant regulatory oversight is also necessary during the handling of cannabis plants, which contain THC – a Schedule I compound in the United States.
Biomedican has developed a patented biosynthetic method of growing rare cannabinoids in proprietary yeast to address this issue. The unique process allows us to extract and purify the most demanded rare cannabinoids.
Biomedican’s patented method creates an engineered strain of yeast, Yarrowia Lypolitica (Y.L.), through sugar and water. This process can be easily upscaled to produce larger volumes of pure rare cannabinoids that can be used in countless products across a wide variety of industries. Our proprietary biosynthesis process and strain of proprietary yeast serve as a reliable source of pure low-cost clinical-grade cannabinoids biologically identical to those found in nature.
Our goal is to make rare cannabinoids widely available at a lower cost, so millions of people can benefit from their unique qualities.
Types of cannabinoid synthesis

1. Grow-harvest method
Human has always been cultivating cannabis plant to get its known active constituents. The output of farmers’ efforts after growing and harvesting cannabis plants was a mixture of cannabinoids containing a small quantity of rare cannabinoids. For example, 10 kilograms of cannabis plants can produce less than 2 grams of rare cannabinoids. This small quantity is not enough to meet a large industry’s requirements. Moreover, this tedious grow-harvest method’s resulting product is impure, costly, and inconsistent. The stringent regulatory requirements such as taxation also contribute to the overall cost of rare cannabinoids.

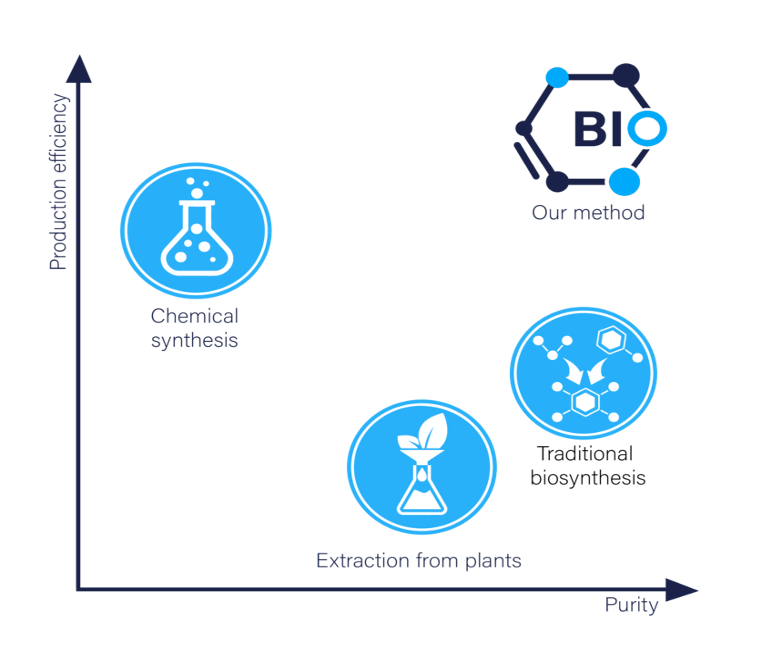
2. Chemical synthesis
Chemical synthesis is the creation of compounds through artificial means by a chemical reaction. The chemical synthesis of rare cannabinoids has become the leading method for the production of these rare, high-value compounds. However, chemical synthesis leads to the production of non-naturally occurring forms of these cannabinoids, which can have unwanted side effects. To overcome the large gap in the supply chain, reduce the environmental footprint, decrease the time of production, circumvent regulatory oversight, and produce high-quality cannabinoids with the exact chemical structures as naturally occurring cannabinoids, Biomedican uses a method of production called biosynthesis.
3. Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a process that has been used for many years in the pharmaceutical and agricultural industries to produce desired compounds in large quantities. Biosynthesis is the production of the desired compound through the natural means of an organism’s biological processes. Biosynthesis produces identical compounds to those found in nature, lending itself as the optimal pathway for the manufacture of cannabinoids and carotenoids identical to their naturally occurring counterparts.
Why is biosynthesis better than other types?
A biosynthetic platform uses the principles of synthetic biology to generate a product. Synthetic biology is defined as “a field of science that involves redesigning organisms for useful purposes by engineering them to have new abilities.”
This technique has allowed scientists and engineers to make great advances, including:
- Modification of rice to produce beta-carotene, which prevents vitamin A deficiency;
- Development of microorganisms that help clean pollution in the soil, water, and air;
- Genetically-engineering yeast that produces rose oil in a sustainable way.
Companies have begun to take advantage of these advances in science and technology to solve manufacturing and medicine problems. Biosynthesis has allowed scientists to manipulate natural processes in organisms to produce a high volume of natural products accurately and sustainably. The adoption of biological synthesis by a vast majority of industries has led to increased efficiency, scalability, and stability of supply. It allows greater flexibility to engineer new patentable molecules for future products.
Biosynthesis of cannabinoids allows their production to be faster, cost-effective, and more sustainable than alternative methods. Biosynthetic cannabinoids grow through naturally occurring processes within a living organism, making them identical to extracted from plants. Also, biosynthetic cannabinoids usually have higher quality, and they are free or almost free of undesirable byproducts.
Opting for a biosynthetic process over a synthetic process achieves the identical composition of the cannabinoid compound in nature while retaining all its benefits without undesirable side effects.
Types of all cannabinoids that can be obtained by biosynthesis
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant. The two most well-known cannabinoids are CBD and THC, which form the entire industry. In addition to those, scientists have already discovered hundreds of cannabinoids. Only a few of them have an intoxicating effect; most cannabinoids, in contrast, offer various health benefits. As the popularity grows and clinical trials commence, new potential uses are continually being discovered.
Let us consider the most important of rare cannabinoids that we can yield through biosynthesis.
Cannabigerol (CBG)
CBG has also recently started to gain traction in the consumer market. This non-intoxicating compound offers unique benefits, specifically amongst inflammation and pain. CBG interacts with the nervous system, creating implications for antiepileptic benefits. In addition, its antibacterial properties have a promising impact on treating digestive conditions. Expect this cannabinoid to become increasingly more popular in the coming years.
Cannabinol (CBN)
This non-intoxicating compound is naturally present in THC and CBD-rich strains of Cannabis sativa. CBN shows promise for positive impacts on appetite, neurological health, and potentially sleep. At this time, there is not enough evidence to draw definitive conclusions around this cannabinoid’s effect on sleep, but the results of ongoing studies will provide more details.
Cannabichromene (CBC)
The CBC compound has been heavily researched over the past few decades but is still relatively hard to extract from the plant. Limited lab studies revealed that it appears to interact with the brain to modulate the sensation of pain and promote brain health without causing intoxication. Due to the difficulty in obtaining this compound, there are not many products that prominently consist of this cannabinoid. However, there is evidence that including this compound may contribute to a theory called the entourage effect. This theoretical form of synergy between cannabinoids may further promote the benefits when they are used together.
Cannabidivarin (CBDV)
CBDV is structurally similar to CBD but is different enough to be classified separately. This compound is mostly known for its potential antiepileptic benefits and has been researched for its ability to treat inflammation, pain, and neurological disorders. This rare compound is only present in the cannabis plant in minimal amounts but may strengthen other cannabinoids’ interaction through the entourage effect.
Cannabigerovarin (CBGV)
CBGV is an analog of CBG and has similar properties but is lesser-known and is only available in tiny quantities within a cannabis plant. Initial studies have shown that it may have the unique property of increasing the bioavailability of CBD, or in other words, may enhance the effects. This compound has also shown potential digestive, antibacterial, and glaucoma fighting benefits.
Other potential rare cannabinoid applications may include anti-stress and minimizing the effects of PTSD and lifesaving benefits like cancer and asthma treatment and reducing a patient’s chances of rejection of an organ transplant. These cannabinoids also offer a greater delivery rate as they can access the blood-brain barrier via the endocannabinoid system.
THCA (Tetrahydro cannabinolic acid)
THCA (Tetrahydro cannabinolic acid) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis. It comes from the “mother of all cannabinoids” – cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). Enzymatic reactions in different strains of cannabis convert CBGA into tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), and cannabichromene acid (CBCA). THCA is present in variable quantities in cannabis.
Cannabinoids produced by BioMedican
Biomedican’s cutting-edge biotechnology methods are remodeling the production of high-value compounds. Our team of dedicated scientists has genetically optimized yeast to produce cannabigerol (CBG), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), other rare cannabinoids, and analogs. These biosynthetic compounds are pharmaceutically pure and 100% identical to ones found in nature at a fraction of their cost, making them promising contenders to replace synthetic and plant-extracted analogs.
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA)
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is the non-psychoactive cannabinoid within the Cannabis plant from which tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is derived. THCA does not cause the sensation of a high and shows therapeutic promise through its anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, and neuroprotective properties.

THCA works through the endocannabinoid system to exert it’s health-promoting effects. Due to these numerous health benefits, the food industry has also taken advantage of THCA. Cannabis tea has become increasingly popular with THCA being one of the most abundant cannabinoids present within the Cannabis plant.

Fights inflammation
Inflammation can worsen conditions like arthritis, liver disease, and inflammatory bowel disease. By supporting optimal balance of inflammatory molecules, including COX-1 and COX-2, THCA can alleviate inflammation.

Supports digestion
Exposure to certain molecules, such as chemotherapy agents, can elicit nausea and vomiting. By interfering in this process, THCA can defend against nausea and vomiting.

Protects the brain
Though inflammatory damage can lead to devastating neurological conditions, THCA exhibits neuroprotective potential. By activating the PPARγ receptor, THCA can promote the optimal regulation of brain inflammation and support a healthier response to inflammatory damage.
Defends against cancer
Oxidative stress can disrupt the immune system and can lead to activation of cancer cells. By neutralizing oxidative stress and regulating inflammation, THCA can enhance immune defense and promote the destruction of cancer cells.
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA)
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is one of the 113 cannabinoids found within the cannabis plant and is an analog to its well-known counterpart, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). THCV and its precursor tetrahydrocannabivarin acid (THCVA) reduce appetite, assist sugar metabolism, have neuroprotective properties, and stimulate the body’s ability to grow bone.

THCV targets the endocannabinoid system to promote health and wellness.

Supports digestion and weight loss
As a cannabinoid, THCV targets the endocannabinoid system, which is linked to hunger and satiety. By regulating receptors in the gastrointestinal (G.I.) tract, THCV can
- Promote the balance of food intake and aid in weight loss.
- Promote optimal sensitivity to insulin, sugar metabolism, and energy usage.
- Defend against chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting by regulating the body’s G.I. reaction to chemical particles.

Protects the brain
THCV is well-known for its neuroprotective effects on the brain, and can
- Promote the activation of a major mood hormone called serotonin, which can defend against the excess movement seen in conditions like schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease.
Support the balance of ions in the brain and promote suppression of seizure activity in epilepsy. - Defend against addiction behavior, through the anti-nicotine properties of THCV.

Promotes skin and bone health
A therapeutic avenue that has been of interest to the cosmetic and orthopedic pharmaceutical industries is the effect of THCV on musculoskeletal wellness and remodeling. This is because THCV can support the stimulation of bone marrow cells and the synthesis of bone.
Cannabigerol/Cannabigerolic Acid (CBG/CBGA)
Although Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the most popular forms of medical cannabis, increasing research suggests that Cannabigerol (CBG), another molecule found in cannabis plants, has significant and unique health benefits. CBG and its precursor, Cannabigerolic Acid (CBGA), can stimulate bone growth, optimize microbial defense, and augment overall wellness.

As an antioxidant that targets the endocannabinoid system, CBG exhibits a wide array of health benefits. The benefits of CBG have also been researched for use in aquaculture. CBG has been leveraged for its effects on bioluminescence, pigment production, motility, and biofilm formation in marine bacteria.

Promotes pain relief
This significant health benefit has sparked a renewed interest in the pharmaceutical industry towards the molecular chemistry of CBG. CBG powerfully targets transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, which are well-known to be linked to the perception of pain. By regulating pain perception, CBG can promote analgesia without causing a high

Protects the brain
Oxidative stress can damage both cells and the immune system and can lead to neurological conditions. By acting as a potent antioxidant and neutralizing oxidative stress, CBG can prevent the loss of brain cells and help to
- Support muscle function and movement in Huntington’s disease
- Prevent immune cell overactivation that can worsen multiple sclerosis.
- Support the recovery of nigrostriatal brain cells in Parkinson’s disease.

Supports the destruction of cancer cells
Oxidative stress can damage the immune system, cause early cell death, and activate cancer cells. By neutralizing oxidative stress, CBG can help promote the death of cancer cells.
Cannabinol/Cannabinolic Acid (CBN/CBNA)
Cannabinol (CBN) is one of over 100 cannabinoids naturally found within the Cannabis plant. CBN is a rare cannabinoid produced at low levels within the cannabis plant and is uniquely derived from the breakdown of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). CBN and its precursor cannabinolic acid (CBNA) help regulate sleep and mitigate pain, inflammation, and neurological, digestive and skin conditions.


Promotes optimal digestion
CBN targets the endocannabinoid system, which links various parts of the body, such as the brain and gastrointestinal (G.I.) tract. Overactivation of the G.I. tract can worsen conditions, such as Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis. By regulating digestion, CBN can help prevent overactivation of the G.I. tract

Defends the skin
CBN has been harnessed within dermatology and cosmetology. By decreasing levels of inflammatory molecules, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukins, CBN/CBNA can help promote a healthy inflammatory response in conditions, such as dermatitis, acne, and skin cancer.

Protects the brain
The effects of CBN/CBNA on the brain and nervous system have also been investigated for its potential in neurological conditions. By protecting the brain from oxidative stress, CBN can promote movement in conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)

Supports the immune system
Oxidative stress can disrupt the immune system and cause the immune system to overreact against the body. By neutralizing oxidative stress, CBN can support healthy immune function and promote defense against autoimmune conditions

Promotes pain relief
CBN/CBNA has been extensively studied by the pharmaceutical industry for its pain-relieving effects. By increasing the threshold at which pain is felt, CBN can promote analgesia.
Method of cannabinoid biosynthesis from yeast
Biosynthesis relies on the naturally occurring biological processes of organisms to generate products. The most common biosynthetic platforms use yeast strains (e.g., Saccharomyces cerevisiae) or Escherichia coli (E. coli). These organisms can be easily manipulated to synthesize natural products accurately and without much human intervention. Biosynthetic compounds are 100% pure and contain no unnatural components. These platforms are also much cheaper, faster, and more environmentally sustainable than traditional chemical synthesis methods.
Biosynthesis relies on the naturally occurring biological processes of organisms to generate products. The most common biosynthetic platforms use yeast strains (e.g., Saccharomyces cerevisiae) or Escherichia coli (E. coli). These organisms can be easily manipulated to synthesize natural products accurately and without much human intervention. Biosynthetic compounds are 100% pure and contain no unnatural components. These platforms are also much cheaper, faster, and more environmentally sustainable than traditional chemical synthesis methods.
Some examples of biosynthetic platforms and their products include:
- Chemicals and biofuels: Research has investigated using the fungal species Aspergillus to produce chemicals and biofuels, providing a much more sustainable option than fossil fuels.
- Plant secondary metabolites: The strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been engineered to produce plant secondary metabolites, often difficult to make via chemical synthesis.
- Tropane alkaloids (T.A.s): The strain cerevisiae has also been engineered to produce T.A.s, which are used to treat cardiac arrhythmias, symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, and nerve agent poisoning.
We thought, what if yeast can grow rare cannabinoids? Yeast is widely used for the biosynthesis of high-value compounds so that it may work for cannabinoids.
Well, there are a few challenges here:
- Cannabinoids require oil. Rare cannabinoids possess a variety of qualities that benefit humans, including antibacterial and antifungal properties. Unfortunately, the same aspects make them toxic to both plants and yeasts. In nature, the cannabis plant releases these cannabinoids in oily droplets found outside of the plant cells, called trichomes, to alleviate toxicity by diluting them in oils. Moreover, oils and cannabinoids use the same precursors for production; therefore, the higher the volume of oils produced, the more cannabinoids will be present. Can yeast do the same?
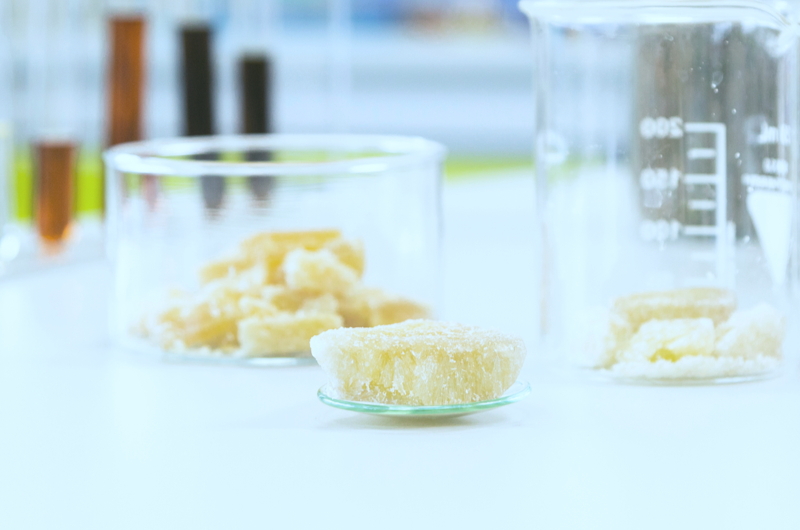
Yes, we use the particular type of yeast – oily yeast Yarrowia Lypolitica (Y.L.), which produces more massive oily drops inside their cells, containing more significant amounts of cannabinoids than others yeast. Our patented method uses the specially engineered Y.L. strain that produces up to 80% of its weight in oils.
- Increasing yield.The second challenge is that naturally occurring Y.L. contains unmutated NhpB synthase, producing low levels of CBGA with large amounts of undesirable byproducts. We used bioengineering methods to address this. By switching to the NphB enzyme, which creates more than 99% CBGA with higher efficiency and activity than the unmutated form, we significantly increased the yields.
- Besides, fermentation we use has also been shown to be 2-5 times more productive than commonly used batch feed. We also use sugar as an inexpensive carbon source, which makes CBGA production highly efficient.
The result: high quality and high quantity of rare cannabinoids
By creating a strain of oily yeast that contains these compounds, we achieved a greater yield, higher quality, and a more sustainable production process. This process can be easily upscaled to produce larger volumes of pure rare cannabinoids that can be used in countless products across a wide variety of industries. Using a biosynthetic method to create these cannabinoids will ultimately allow these beneficial compounds to reach more people while minimizing environmental impact, cost, and resources. Our proprietary biosynthesis process and strain of proprietary yeast serve as a reliable source of pure low-cost clinical-grade cannabinoids biologically identical to those found in nature.
The market value of biosynthetic cannabinoids
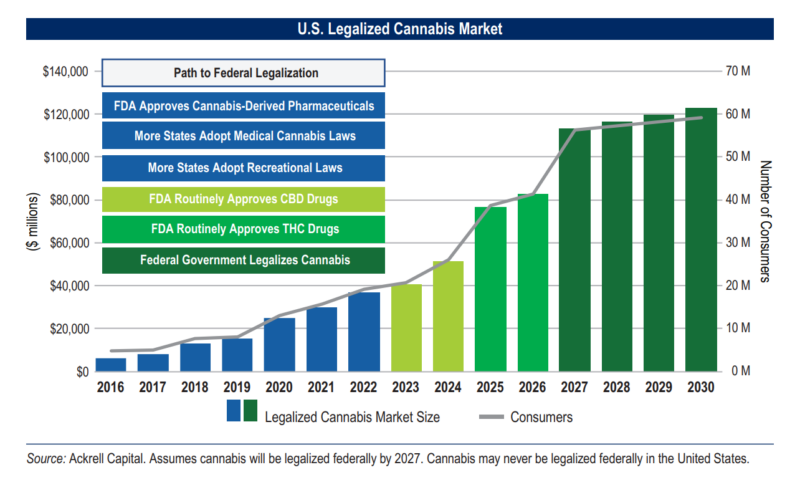
Cannabinoids fit into a multitude of diverse and rapidly expanding markets:
- The adult-use and medical cannabinoid market is projected to reach $146.4 billion by 2025 globally.
- By 2022 the cannabinoid-infused edible and beverage industry is predicted to surpass $30 billion.
- The cannabinoid-based pharmaceutical global market is expected to hit $50 billion by 2029.
For this growth to occur, the market demands high-purity low-cost products. The current production methods are insufficient to meet this projected demand, as rare cannabinoids are not produced in large quantities by cannabis plants — the conventional vehicles for making and extracting such compounds.
The pharmaceutical potential of cannabinoids cannot be overstated, as the efficacy of cannabinoids has been implicated in treating pathologies with billion-dollar markets in the U.S. alone. Our low-cost production of such high-value compounds will generate a competitive advantage over traditional forms of treatment for diabetes, cancers, autoimmune disorders, respiratory disease, nervous system disorders, pain, viruses, ADHD, and more.
Benefits of investing in cannabinoids biosynthesis with BioMedican
The white biotechnology sector is devoted to the sustainable industrial production of compounds with high societal value. As the cannabinoid market surges, the therapeutic value of hundreds of cannabinoids is coming to light. It is their potential to impact the quality of life of many patients.
Biomedican generates cannabinoids and terpenes directly from proprietary yeast without costly plant cultivation or inefficient extraction and purification procedures in a scalable fashion. Production facilities for biosynthesis cost a fraction of traditional cannabis facilities enabling much more cost-efficient manufacturing.
Our biosynthesis platform is positioned to disrupt the largest $1B+ and fastest-growing markets, including the market of biosynthetic cannabinoids projected to reach $10B by 2025:
- 99% pharmaceutical grade compounds
- 100% organic/non-GMO
- Highest yields and lowest costs in the industry – 70-90% less than the current wholesale market
- More sustainable – utilizes 90% less energy and natural resources
- Bioidentical to the molecules found
- Unique and exclusive I.P. – four U.S. patents pending
- Four Ph.D. scientists lead our research team in biosynthesis and genetics
- CBG/CBGA is ready for large scale production
- THCV/THCVA and CBN/CBNA are expected to be ready for production by Q2 2022
- Global distribution via large CBD networks, nutraceutical, cosmetic/lotions manufacturers
Biomedican research and production strategies are continuously improving. Our intellectual property portfolio keeps growing as we aim to streamline the production pipeline of pure and consistent compounds that are in high demand across many regions in the U.S. and Canada.
Investors benefit from the ability to participate in an industry currently gaining enormous momentum. Our proprietary technology can revolutionize the cannabinoid supply chain and directly feed into several markets where cannabinoids and terpenes are in high demand. As the production of cannabinoids and terpenes through biosynthesis is significantly quicker than traditional methods, investors can expect a faster return on investments.




